Foraminal Stenosis
Foraminal Stenosis
What is Foraminal Stenosis?
- Similar to spinal stenosis
- If ignored, can result in loss of function
- We treat with minimally invasive, simple laser surgery
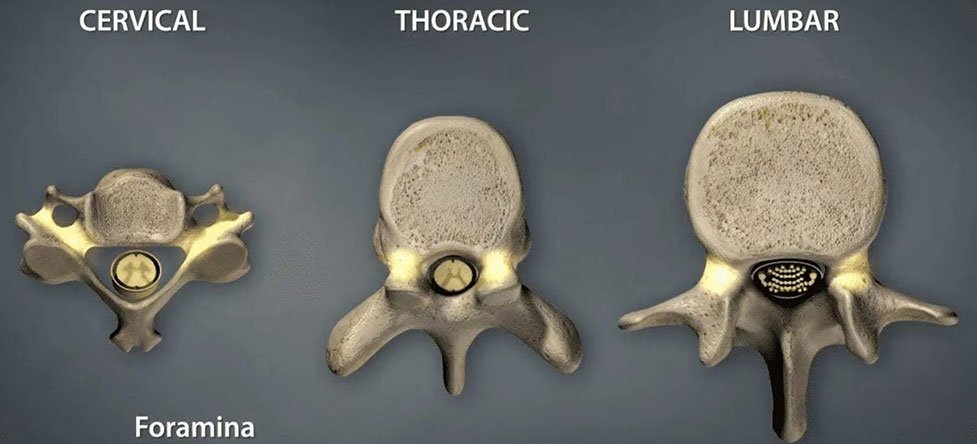
Up and down the spine, nerve roots extend from the spinal cord and exit the spinal column through small canals (foraminal canals). Foraminal stenosis is the narrowing of these canals.
Foraminal stenosis primarily affects one or more areas of your spine. When looking at the normal spine, there is enough room for the nerve roots to slip through the canals. However, the canals can become clogged with debris as we age, trapping debris that narrows the canals, compressing the nerves.
Our Treatment Approach
Our back and spine specialists use a simple laser with minimally invasive techniques to treat the blockage of debris, relieving the pain and reinstating normal function. We don’t cut any muscle to get to the clogged canals, so there is no trauma to surrounding tissue and recovery time is generally faster with less pain.
Our goal is to have you back to enjoying life as quickly as possible.
Causes
The primary cause of foraminal stenosis is ageing. The wear and tear of daily activity can create debris that collects in the foraminal canals causing them to narrow and press on nerves. Other causes include:
- Bone spurs
- Herniated disc
- Bulging disc
- Arthritis
- Ligament thickening.
Symptoms
Your symptoms may include pain that radiates into the thigh, calf and possibly the foot from a spinal nerve. The pain can be deep and lasting. Certain movements such as sitting and walking can elicit pain.
The pain can be accompanied by numbness, tingling, weakness, sensations of burning and pins and needles pricks in the affected extremity.
Cervical spinal stenosis does not always cause symptoms. It is possible to have cervical foraminal narrowing that is visible on medical imaging, such as an MRI, without any associated pain or neurological deficits. The underlying factors as to why some people with cervical foraminal stenosis have symptoms and others do not is still being researched.
